Music
Trailers
DailyVideos
India
Pakistan
Afghanistan
Bangladesh
Srilanka
Nepal
Thailand
StockMarket
Business
Technology
Startup
Trending Videos
Coupons
Football
Search
Download App in Playstore
Download App
Best Collections
Technology
Uber is reportedly developing a short-term staffing business to offer 1099 independent contractors for events and corporate functions, the Financial Times first reported. Dubbed Uber Works, the service would provide waiters, security guards and other temporary staffers to business partners, a source close to Uber told TechCrunch.
Uber has been working on the project for several months in Chicago, after first trialing the project in Los Angeles.Uber already has a vast network of drivers — all of whom have become familiarized with the process of filing taxes as an independent contractor — who may be looking for additional work. However, Ubercurrent pilot program does not include active Uber drivers.
Uber Works falls under the purview of Rachel Holt, who stepped into the role of head of new modalities in June. Holt, who has been with Uber since 2011, is tasked with ramping up and onboarding new mobility services like bikes, scooters, car rentals and public transit integration.
In a job posting for a general manager to lead special projects in Chicago, Uber says, &our business is based around providing a flexible, on-demand supply for our business partners & itimperative that we have intuitive and responsive account management to support for our business partners in addressing their needs promptly.&
Uber declined to comment for this story. But as the company gears up for its initial public offering next year, Uber is clearly trying to diversify its business. In the last year, Uber double-downed on multi-modal transportation with the acquisition and deployment of JUMP bike-share. And in the last month, Uber deployed electric scooters in Santa Monica, Calif.
Whether this effort launches remains to be seen, but itcertainly something Uber is exploring and positioning as a business-to-business service. In a similar vein, Uber is also working to create a pipeline to hire some of its driver partners.
- Details
- Category: Technology
Read more: Uber is developing an on-demand staffing business
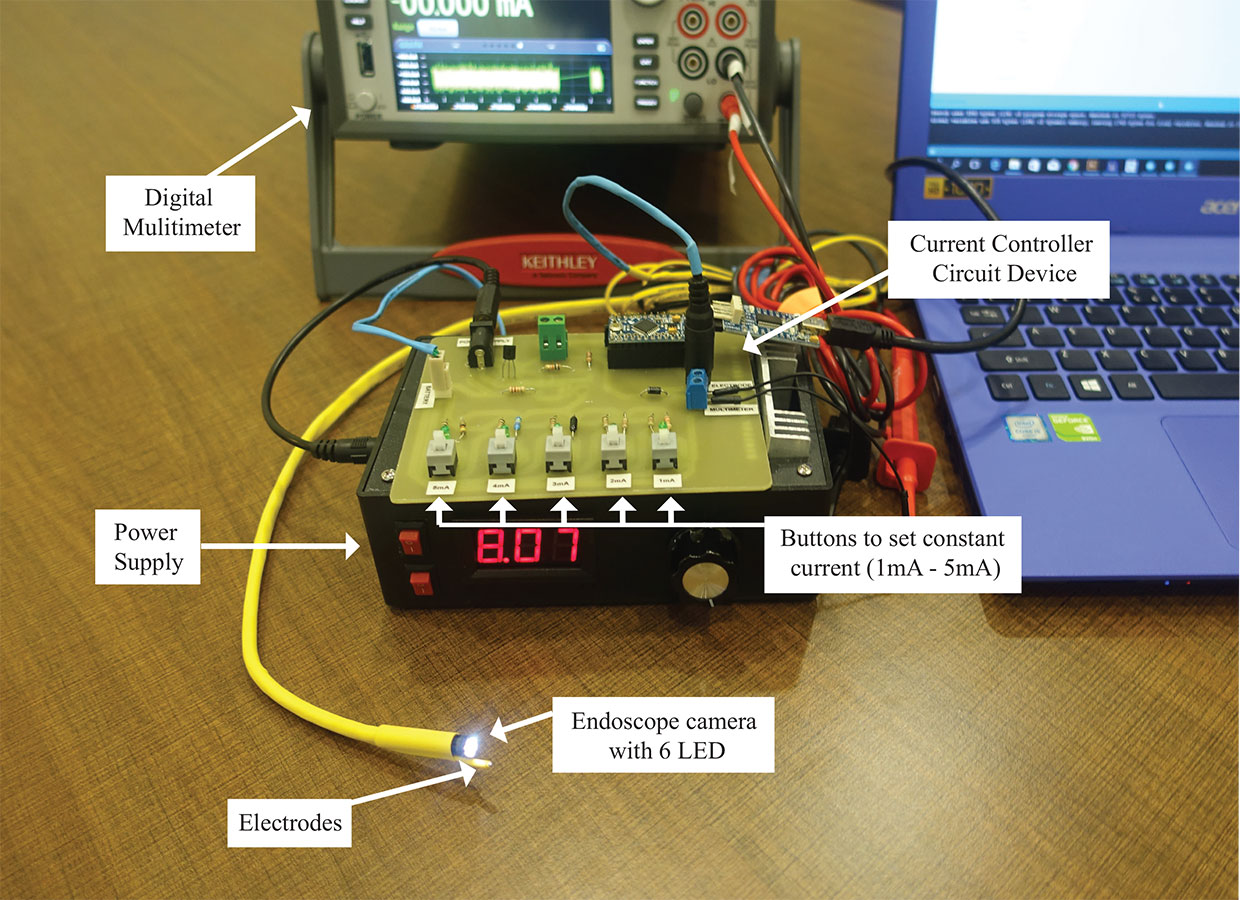
Write comment (100 Comments)The IEEE has showcased one of the coolest research projects I&ve seen this month: virtual smells. By stimulating your olfactory nerve with a system that looks like one of those old-fashioned kids electronics kits, they&ve been able to simulate smells.
The project is pretty gross. To simulate a smell, the researchers are sticking leads far up into the nose and connecting them directly to the nerves. Senior research fellow at the Imagineering Institute in Malaysia, Kasun Karunanayaka, wanted to create a &multisensory Internet& with his Ph.D. student, Adrian Cheok. Cheok is Internet famous for sending electronic hugs to chickens and creating the first digital kisses.
The researchers brought in dozens of subjects and stuck long tubes up their noses in an effort to stimulate the olfactory bulb. By changing the intensity and frequency of the signals, they got some interesting results.
The subjects most often perceived odors they described as fragrant or chemical. Some people also reported smells that they described as fruity, sweet, toasted minty, or woody.
The biggest question, however, is whether he can find a way to produce these ghostly aromas without sticking a tube up peoplenoses. The experiments were very uncomfortable for most of the volunteers, Karunanayaka admits: &A lot of people wanted to participate, but after one trial they left, because they couldn&t bear it.&
While I doubt we&ll all be wearing smell-o-vision tubes up our noses any time soon, this idea is fascinating. It could, for example, help people with paralyzed senses smell again, a proposition that definitely doesn&t stink.
- Details
- Category: Technology
Read more: Researchers create virtual smells by electrocuting your nose
Write comment (97 Comments)The hypearound quantum computing is real. But to fully realize the promise of quantum computing, it&ll still take a few years of research and scientific breakthroughs. And indeed, it still remains to be seen if quantum computers will ever live up to the hype. Today, though, we got mathematical proof that there are reallycalculations that quantum computers will definitely be able to perform faster than any classical computer.
What we have today are quantum computers with a very limited number of qubits and short coherence time. Those limitationsput a damper on the amount of computation you can perform on those machines, but they still allow for some practical work. Unsurprisingly, researchers are very interested in seeing what they can do with the current set of available machines. Because they have such short coherence time before the system becomes chaotic and useless for any computations, you can only perform a relatively small number of operations on them. In quantum computing speak, that&depth,& and todaysystems are considered shallow.
Science today published a paper(&Quantum advantage with shallow circuits&) bySergey Bravyi of IBM Research, David Gosset of the University of WaterlooInstitute for Quantum Computing and Robert König of the Institute for Advanced Study and Zentrum Mathematik, Technische Universität München. In this paper, the researchers prove that a quantum computer with a fixed circuit depth is able to outperform a classical computer thattackling the same problem because the classical computer will require the circuit depth to grow larger, while it can stay constant for the quantum computer.
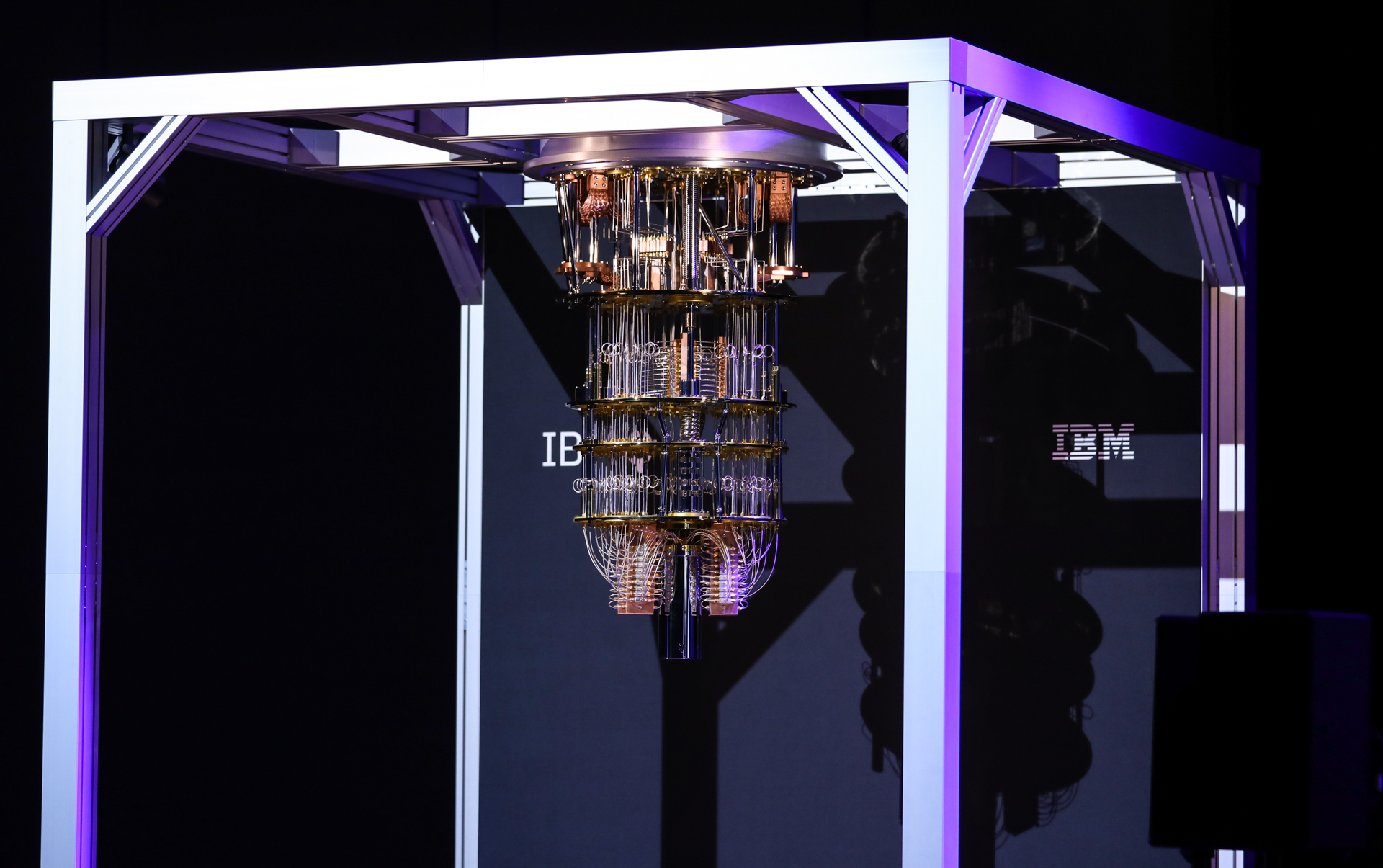
There is very little thatintuitive about quantum computing, of course, but itworth remembering that quantum computers are very different from classical computers.
&Quantum circuits are not just basically the same but different from classical circuits,& IBMQ Ecosystem and Strategy VP Bub Sutor told me. Classic circuits, […]they arebits, they arezeros and ones, andthere&s binary logic, ANDs, ORs, NOTsand things like.Thevery, very basic gate sets,the types of operationsyou can do in quantum are different. When these qubitare actually operating,withthis notion of superposition you have much, much more to operate elbow room, not justtwo bits. You actually have a tremendous amount of more room here.& And itthat additional room you get, because qubits can encode any number and not just zeros and ones, that allows them to be more powerful than a classical computer in solving the specific kind of problem that the researchers tackled.
The question the researchers here asked was if constant-depth quantum circuits can solve a computational problem that constant-depth classical circuits cannot The problem they decided to look at is a variation on the well-known Bernstein-Vazirani problem (well-known among quantum computing wonks, that is). You don&t need to jump into the details here, but the researchers show that even a shallow quantum computer can easily outperform a classical computer in solving this problem.
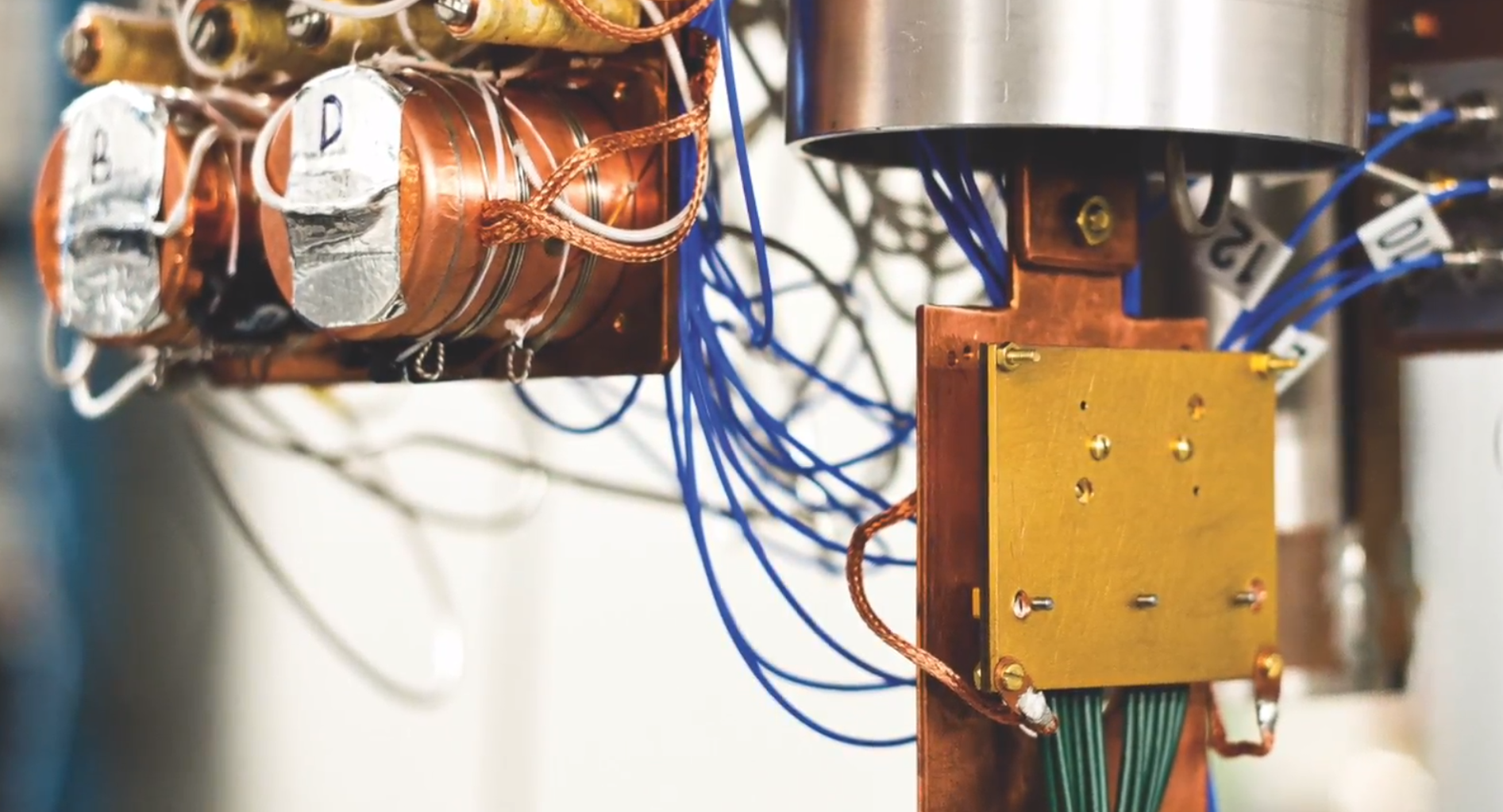
&We tried to understand what kinds of things we can do with a shallow quantum circuit and looked for an appropriate model for a type of computation that can be done on a near-term quantum device,& Bravyi told me. &What our result says is that there are certain computational problems for which you can solve on a quantum computer with a constant depth. So as you increase the number of input bits, the depth of the quantum algorithm that solves the problem remains constant.& A constant depth classical computer can not solve this problem, though.
Sutor was very quick to note that we shouldn&t over-hype the current state of quantum computing or this result, though. &We try to be extremely cautious and honest in terms of saying ‘this is what quantum computers can do today& versus what classical computers will do,& he told me. &And we dothis foravery specific reason in that thatthisis something that will play out over the next three to five years and decades —probably decades.& But what this result shows is that itworth exploring quantum algorithms.
As Sutor noted, &there is still this core question, which is, ‘why are you bothering'& Todayresult should put that question to rest, but Sutor still stressed that he tries to stay grounded and never says quantum computing &will& do something until it does. &Therea strategy through this, but theregoing to be little left turns and right turns along the way.&
- Details
- Category: Technology
Read more: There’s now proof that quantum computers can outperform classical machines
Write comment (97 Comments)If you&re heading out to meet someone, there are plenty of ways to inform them of your location and estimated arrival. Chat apps like WhatsApp, Messenger, LINE and iMessage, for example, offer location-sharing functionality, while navigation apps like Waze and CityMapper and even ridesharing apps like Uber offer live updating ETAs. Now, Google Maps& own ETA feature is at last coming to iOS. The feature is also getting a few tweaks following last yearlaunch on Android, the company says.
In May 2017, Google Maps first introduced its own take on location and ETA sharing.
From a &Share Location& option in the appmain navigation bar, you&re able to pick how long you want to share your location and choose with whom to share it — the latter from a set of frequent contacts or by entering someonename, number or email to pull from your address book.
Then, from the navigation screen, another option called &Share trip progress& allows users to share their live ETA with others as they start their trip.
Today, Google is bringing this ETA feature to Google Maps on iOS.
To try it out, tap on the ˄ button once you&ve begun navigation, then tap &Share trip progress.& This will allow you to share with favorite contacts your live location, route and your ETA, as before.
However, the feature is also being improved with todayrelease to allow for sharing across third-party apps like Messenger, WhatsApp, LINE and others. That makes it easier to include in your text message threads and group chats, which are probably already underway.
The feature works for driving, walking and cycling navigation, says Google. Itlive now on iOS and Android.
- Details
- Category: Technology
Read more: Google Maps’ ETA sharing feature hits iOS
Write comment (96 Comments)Google is launching a number of new features for Android app developers today that will make it easier for them to build smaller apps that download faster and to release instant apps that allow potential users to trial a new app without having to install it.
Android App Bundles, a feature that allows developers tomodularizetheir apps and deliver features on demand, isn&t a new feature. The company announced it a while ago; there are now &thousands of app bundles& in production with an average file size reduction of 35 percent. With todayupdate, Google is making some changes to how app bundles handle uncompressed native libraries that are already on a device. Those will lead to downloads that are on average 8 percent smaller and take up 16 percent less space on a device.
Talking about size, Google now lets developers upload app bundles with installed APK sizes of up to 500 megabytes, though this is currently still in early access.
In addition, App Bundles are now supported in Android Studio 3.2 stable and Unity 2018.3 beta.
While small app sizes are nice, another feature Google is announcing today will likely have a larger impact on developers and users alike. Thatbecause the company is making some changes to Instant Apps, a feature that allows developers to ship a small part of their apps as a trial or to show a part of the app experience when users come in from search results — and thereno need to download the full app and go through the (slow) install procedure.
With this update, Google is now using App Bundles to let developers build their instant apps. That means they don&t have to publish both an instant app and an installable app. Instead, they can enable their App Bundles to include an instant app and publish a single app to the store. Thanks to that, therealso no additional code to maintain.
Developers also can now build instant apps for their premium titles and publish them for their pre-registration campaigns, something that wasn&t previously an option.
Other updates for Android developers include improved crash reports that now combine real-world data from users with that from the Firebase Test Lab when Google sees those crashes under both circumstances. There also are updates to how developers can set up subscription billing for their apps and a couple of other minor changes you can read about here.
- Details
- Category: Technology
Read more: Google improves Android App Bundles and makes building Instant Apps easier
Write comment (95 Comments)Twilio is hosting its Signal developer conference in San Francisco this week. Yesterday was all about bots and taking payments over the phone; today is all about IoT. The company is launching two new (but related) products today that will make it easier for IoT developers to connect their devices. The first is the Global Super SIM that offers global connectivitymanagement through the networks of Twiliopartners. The second is Twilio Narrowband, which, in cooperation with T-Mobile, offers a full software and hardware kit for building low-bandwidth IoT solutions and the narrowband network to connect them.
Twilio also announced that it is expanding its wireless network partnerships with the addition of Singtel, Telefonica and Three Group. Unsurprisingly, those are also the partners that make the companySuper SIM project possible.
The Super SIM, which is currently in private preview and will launch in public beta in the springof 2019, provides developers with a global network that lets them deploy and manage their IoT devices anywhere (assuming there is a cell connection or other internet connectivity, ofcourse).The Super SIM gives developers the ability to choose the network they want to use or to let Twilio pick the defaults based on the local networks.
Twilio Narrowband is a slightly different solution. Its focus right now is on the U.S., where T-Mobile rolled out its Narrowband IoT network earlier this year. As the name implies, this is about connecting low-bandwidth devices that only need to send out small data packets like timestamps,GPS coordinates or status updates. Twilio Narrowband sits on top of this, using TwilioProgrammable Wireless and SIM card. It then adds an IoT developer kit with an Arduino-based development board and the standard Grove sensors on top of that, as well as a T-Mobile-certified hardware module for connecting to the narrowband network. To program that all, Twilio is launching an SDK for handling network registrations and optimizing the communication between the devices and the cloud.
The narrowband service will launch as a beta in early 2019 and offer three pricing plans: a developer plan for $2/month, an annual productionplan for $10/year or $5/year at scale, and a five-year plan for$8/year or $4/year at scale.
- Details
- Category: Technology
Read more: Twilio launches a new SIM card and narrowband dev kit for IoT developers
Write comment (96 Comments)Page 3898 of 5614

 10
10





